The two pie charts below show some employment patterns in Great Britain in 1992.
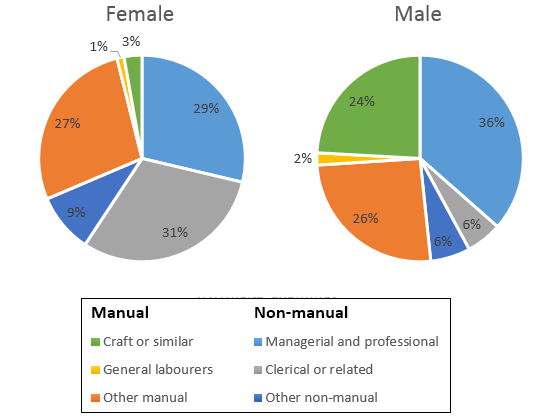
The two pie charts compare the distribution of male and female employment across six distinct manual and non-manual occupational categories in Great Britain in 1992, expressed as percentages.
Overall, men were more heavily represented in managerial, professional, and craft-related roles, while women dominated clerical, other manual, and other non-manual occupations. General labour was the least common occupation for women.
Managerial and professional positions were the most prevalent among men, accounting for 36% of male employment, compared with 29% for women. Crafts and similar occupations were also a significant area for men at 24%, far exceeding the 3% recorded for women. By contrast, clerical and related roles were the leading sector for women, comprising 31% of their workforce, more than triple the proportion for men.
Women also held slightly larger shares in other manual (27%) and other non-manual roles (9%) compared with men (26% and 6%, respectively). General labour, however, employed only 1% of women, making it the smallest category, while the male proportion was noticeably higher.
These patterns highlight a clear gender divide in occupational distribution, with men concentrated in higher-status and skilled manual roles, and women more engaged in clerical and other non-manual work.
Word Count: 174